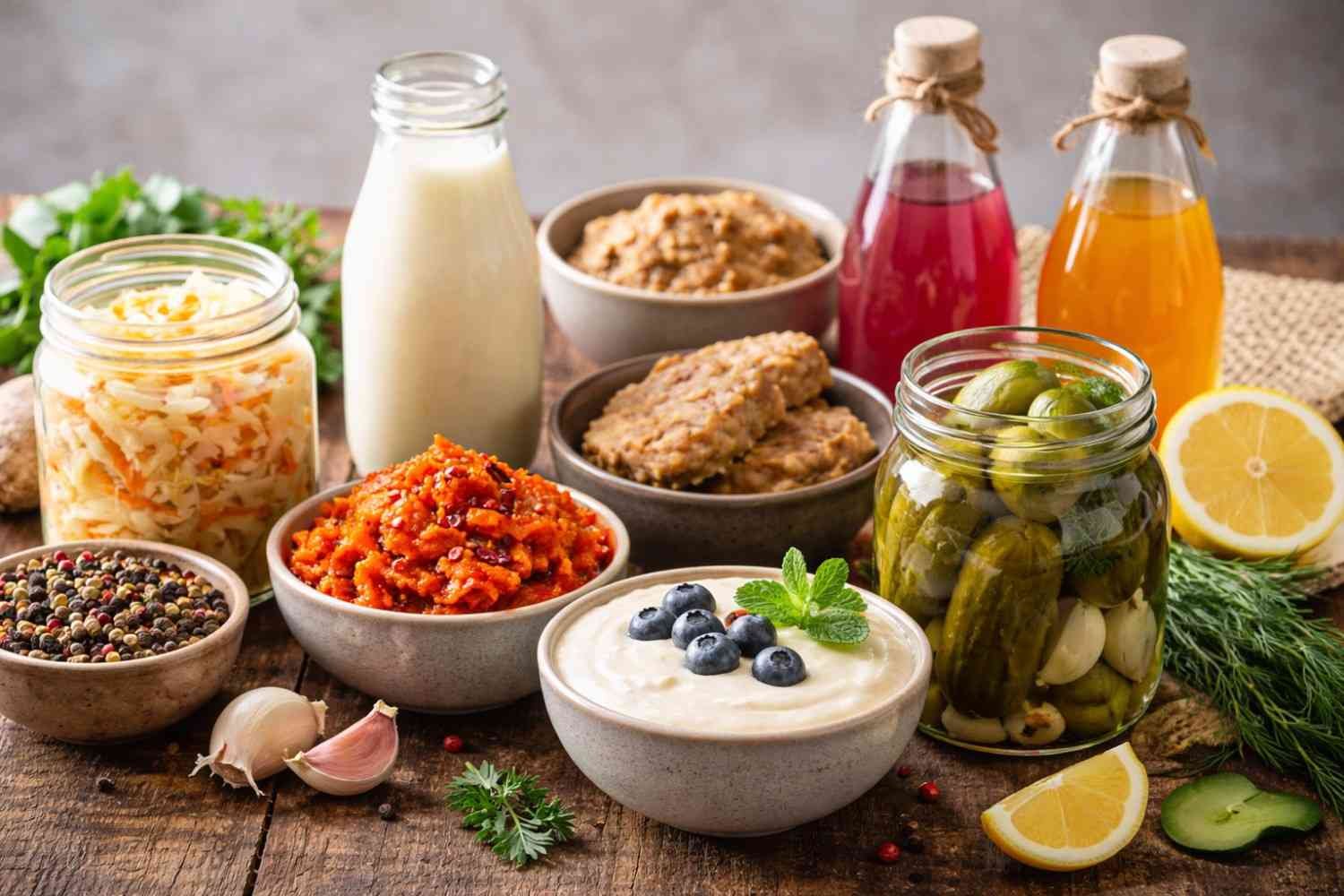
When it comes to superfoods, fermented foods often fly under the radar. However, these foods offer a powerful combination of benefits that support gut health, digestion, immune function, and even mental well-being. Fermented foods like yogurt, kombucha, pickles, and sauerkraut have been part of human diets for centuries, but recent research has brought their health benefits into the spotlight.
We’ll go over the scientifically proven advantages of fermented foods in this post, as well as why they ought to be a regular part of your diet and how they can enhance your general health. Let’s examine the details that justify including these items on your shopping list.
What Are Fermented Foods?
Fermented foods are those that undergo a natural fermentation process involving bacteria, yeast, or fungi. This process helps break down food, preserve it, and enhance its nutritional profile. During fermentation, beneficial microorganisms (probiotics) thrive and create bioactive compounds like organic acids, enzymes, and vitamins.
Some popular examples of fermented foods in the American diet include:
- Yogurt (especially Greek yogurt and probiotic-rich varieties)
- Kefir (a yogurt-like drink)
- Kimchi (Korean-style fermented cabbage)
- Sauerkraut (fermented cabbage)
- Pickles (fermented cucumbers, often enjoyed as a snack or condiment)
- Miso (fermented soybeans, often used in soups and dressings)
- Kombucha (fermented tea drink)
- Tempeh (fermented soy, used in plant-based dishes)
- Sourdough bread (fermented through natural yeasts)
The Top 5 Benefits of Fermented Foods
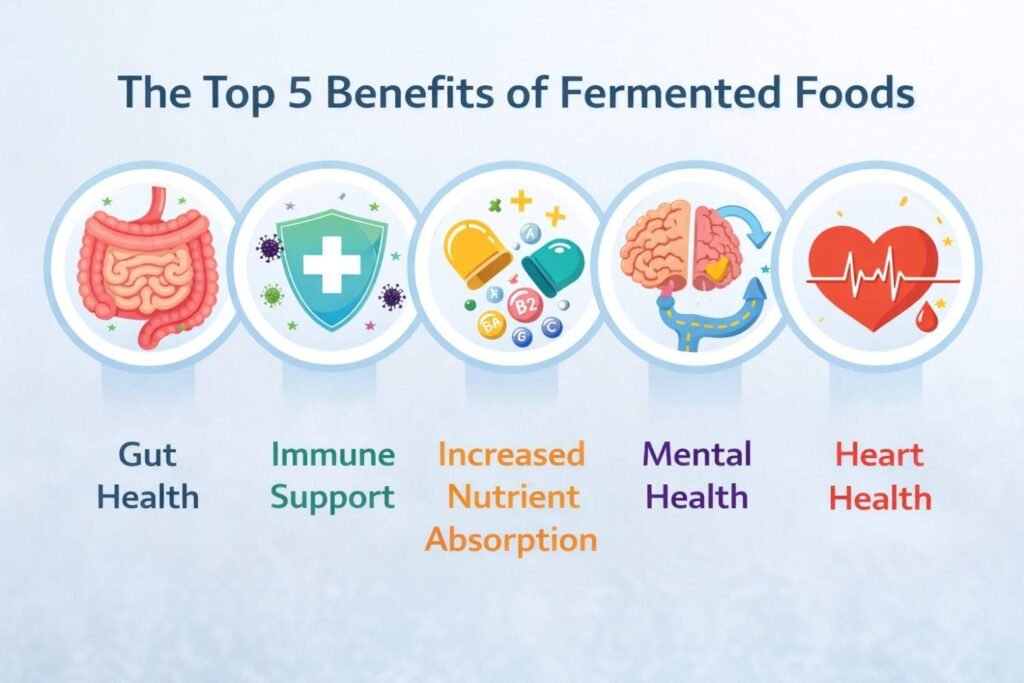
1. Improved Gut Health
The most significant health benefit of fermented foods is their ability to support a healthy gut microbiome. Your gut is home to trillions of bacteria, which play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. The probiotics found in fermented foods replenish and balance the good bacteria in your gut, enhancing digestion and promoting regular bowel movements. They may also help reduce bloating, gas, and other digestive discomforts.
Studies show that the consumption of fermented foods increases microbial diversity in the gut, which is essential for overall digestive health. A balanced microbiome can reduce inflammation and help prevent digestive disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
2. Supports Immune Health
Did you know that about 70% of your immune system is housed in your gut? A well-balanced gut microbiome helps modulate immune responses and maintain a healthy immune system. Fermented foods, rich in probiotics, provide the beneficial bacteria that help support immune function.
Probiotics found in fermented foods boost the production of specific antibodies and support the activity of immune cells like macrophages and T lymphocytes. This can improve your body’s resistance to infections.
3. Increased Nutrient Absorption
Fermentation also breaks down certain compounds in foods, such as anti-nutrients like phytic acid, which can block the absorption of minerals like iron and zinc. As a result, fermented foods make it easier for your body to absorb important nutrients.
Fermentation increases the bioavailability of vitamins like B12 and K2, which are essential for maintaining good health. It also enhances the absorption of minerals like calcium and magnesium.
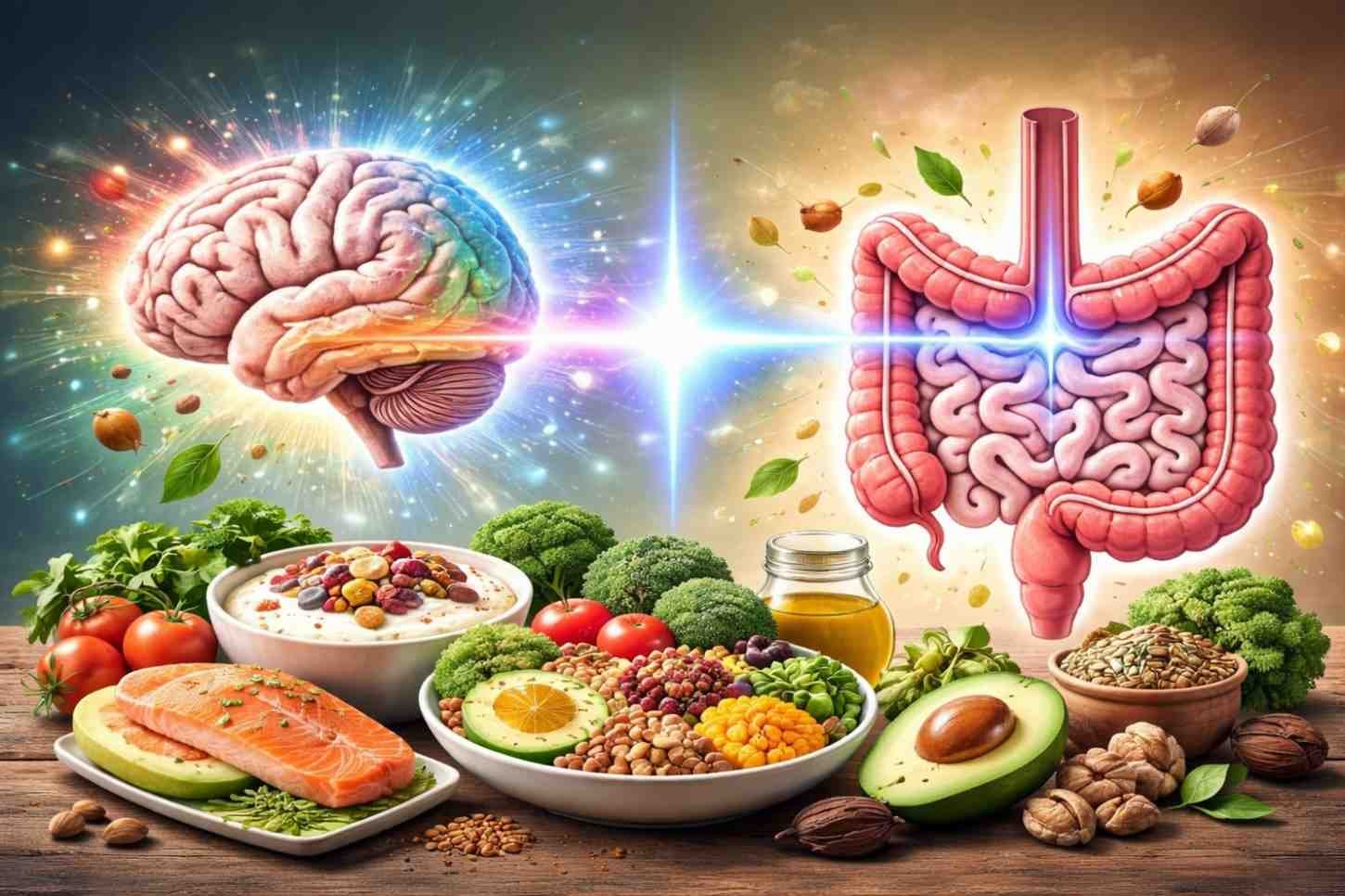
4. Boosts Mental Health
Emerging research is linking the gut to brain health, often referred to as the “gut-brain axis.” The probiotics in fermented foods may influence mood, mental clarity, and cognitive function. Fermented foods have even been shown to potentially reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, thanks to their effects on gut health and the production of neurotransmitters.
Studies show that consuming fermented foods can increase the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood and feelings of happiness. It’s no surprise that fermented foods are sometimes referred to as “food for the brain.”
5. Promotes Heart Health
Heart disease is one of the leading causes of death in the U.S., and fermented foods might help reduce your risk. Some research suggests that the probiotics and bioactive peptides in fermented foods can help lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Fermented foods like yogurt and kefir have been linked with lower cholesterol levels, which can contribute to heart health. They also have anti-inflammatory properties, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Important Considerations

While incorporating fermented foods into your diet can offer many health benefits, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- Live vs. Dead Cultures: Some commercially available fermented foods, such as shelf-stable pickles or canned sauerkraut, undergo heat processing or pasteurization, which can kill the beneficial bacteria (live cultures) that are the source of probiotics. To reap the full probiotic benefits, be sure to look for products that specifically state “live and active cultures” on the label.
- Start Slow: If you’re new to fermented foods, it’s best to start with small servings—like 1 to 2 tablespoons per day—to allow your gut to adjust. Introducing these foods too quickly can lead to temporary bloating, gas, or digestive discomfort as your microbiome adapts.
- Safety Considerations: For individuals with weakened immune systems, histamine intolerance, or certain gastrointestinal conditions, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider before significantly increasing your intake of fermented foods.
How to Incorporate Fermented Foods into Your Diet

Incorporating fermented foods into your diet doesn’t have to be complicated. Here’s how you can easily add these nutrient-packed foods into your daily meals, aligned with typical American food choices:
- Breakfast: Add Greek yogurt or kefir to your smoothie, or top your oatmeal with probiotic-rich yogurt and a handful of berries.
- Lunch: Toss kimchi or sauerkraut onto your salad, or enjoy a miso soup as a side.
- Dinner: Serve tempeh in stir-fries or sandwiches, or enjoy a sourdough roll with your favorite dish.
- Snacks: Sip on kombucha, or snack on pickles and fermented vegetables. These make easy, delicious options that don’t require much preparation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Are the Best Fermented Foods for Gut Health?
The best fermented foods for gut health are those that are rich in probiotics, including Greek yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha. These foods introduce beneficial bacteria to your gut, helping to balance your microbiome and improve digestion.
2. Can Fermented Foods Help with Weight Loss?
Yes, fermented foods may support weight loss by improving digestion and gut health. A healthy gut microbiome can influence factors like metabolism and fat storage, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight.
3. Are All Fermented Foods Good for You?
Not all fermented foods are created equal. Look for unpasteurized, naturally fermented products, as pasteurization can kill the beneficial bacteria. Additionally, watch out for added sugar and high sodium in some fermented foods, which can negate their health benefits.
4. How Much Fermented Food Should I Eat Daily?
Start with a small serving (about 1/4 to 1/2 cup) of fermented food per day and gradually increase it over time as your digestive system adjusts. There’s no one-size-fits-all recommendation, but aiming for 2–3 servings per day is beneficial for most people.
Conclusion
Fermented foods are more than just tasty—they offer a range of health benefits that can improve your gut health, immune function, nutrient absorption, and even mental well-being. Whether you enjoy a daily serving of Greek yogurt, sip on kombucha, or add sauerkraut to your meals, these probiotic-rich foods can be a powerful addition to your diet. Just be mindful of quality, and start slow if you’re new to these foods.