Your immune system is your body’s frontline defense — a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that protects you from infections and helps keep you healthy every day. While there’s no “magic food” that instantly makes you immune to viruses, the foods you eat have a profound impact on how strong and effective your immunity really is.
In this post, we’ll dive deep into scientifically backed nutrition strategies that help support immune function naturally — with meal ideas, practical tips, and the science behind why it works.
Why Nutrition Matters for Immunity
Your immune system doesn’t run on hope — it runs on nutrients. Vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, healthy fats, and protein all play key roles in supporting your immune cells and immune responses. Without the right nutrition, your body has to fight off threats with depleted ammunition.
Healthy eating helps your immune system:
- Build infection-fighting cells
- Reduce chronic inflammation
- Support gut health (a major immune driver)
- Maintain barriers like skin and mucosal linings
- Help immune messaging communicate efficiently within your body
A balanced diet isn’t just “healthier” — it empowers your immune defenses.
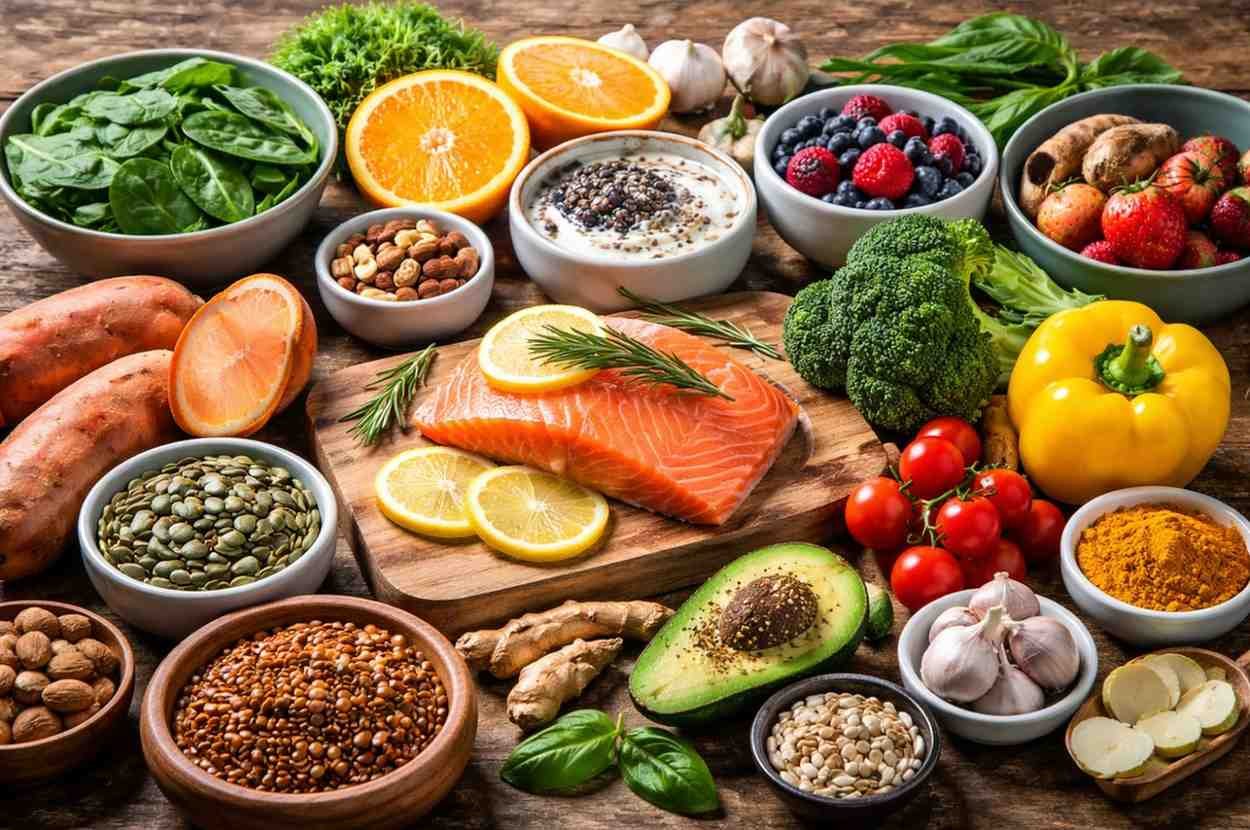
Top Immune‑Boosting Nutrients and What They Do
Here’s a breakdown of the most important nutrients for immune support — and where to find them.
Vitamin C – The Classic Immune Booster
Vitamin C is one of the most studied nutrients linked to immune health. It helps your body produce white blood cells — the fighters that attack pathogens — and supports barrier defenses.
Top food sources:
- Oranges, lemons, grapefruits
- Strawberries, kiwi, papaya
- Bell peppers and broccoli
Experts note that whole fruits are the best option because they deliver fiber and antioxidants along with vitamin C.
Vitamin A & Beta‑Carotene – Protect First‑Line Defenses
These nutrients help maintain healthy skin and mucosal cells — your body’s first physical barrier against infection.
Top food sources:
- Sweet potatoes, carrots
- Spinach, kale
- Apricots and squash
Vitamin D – Sunshine Vitamin with Immune Influence
While sunlight is the main source, many foods contain vitamin D, such as fatty fish, fortified milk, and eggs. Vitamin D influences immune cell activation and inflammation control.
Zinc & Selenium – Critical Mineral Players
Zinc helps white blood cells function and replicate, while selenium helps regulate inflammation and immune messaging.
Food sources:
- Nuts and seeds (especially sunflower seeds)
- Seafood and whole grains
- Brazil nuts (high selenium)
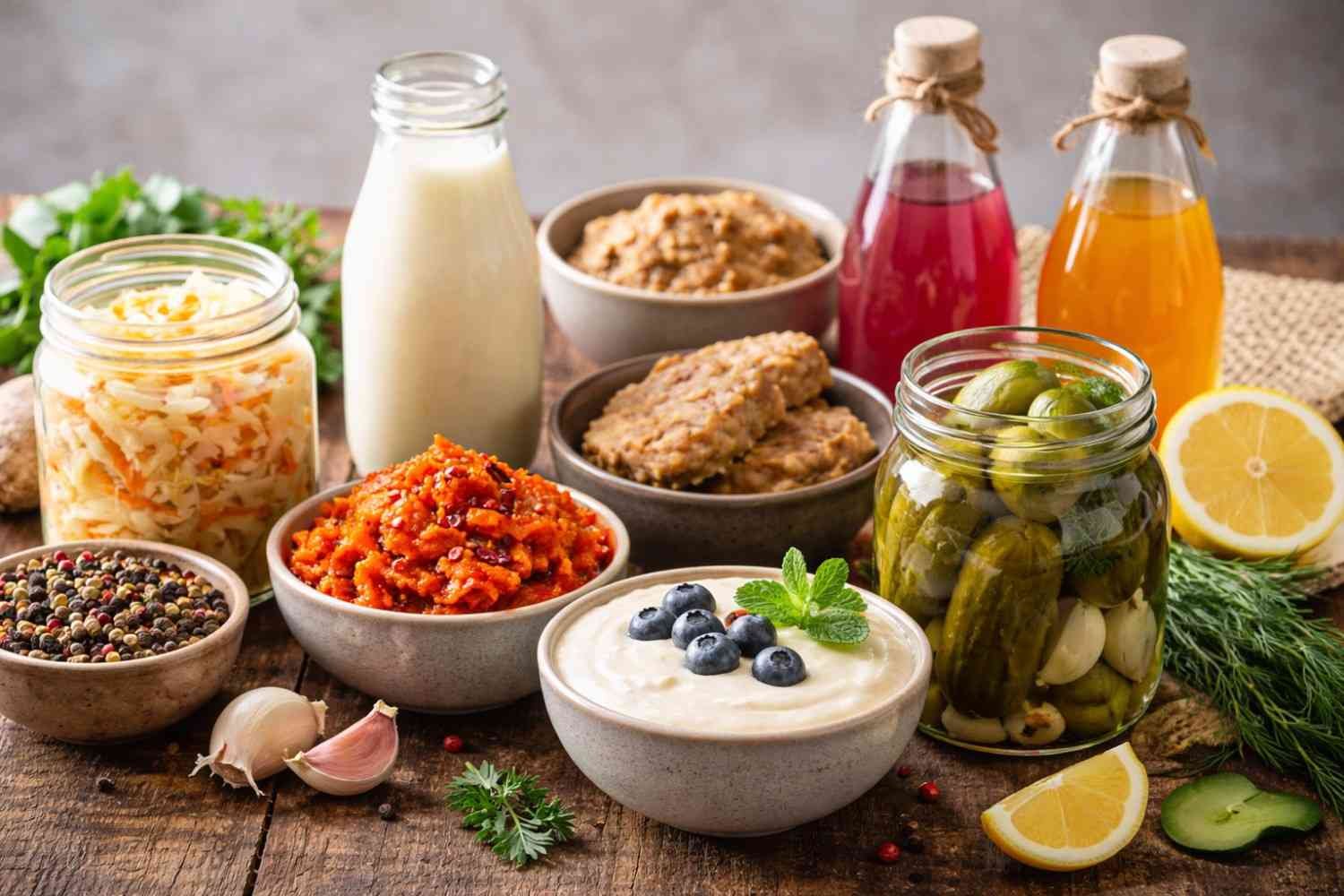
Probiotics – Gut Health Equals Immune Health
About 70% of your immune system lives in your gut. Probiotic foods help feed and balance the gut microbiome, which trains your immune system and maintains pathogen defenses.
Probiotic sources:
- Yogurt with live cultures
- Kefir
- Fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi
12 Best Foods to Include in Your Daily Diet
Here are powerful immune‑support foods backed by science:
- Citrus Fruits – Loaded with vitamin C.
- Berries – Provide antioxidants and flavonoids that support immune pathways.
- Leafy Greens – Vitamin C, beta‑carotene, and folate.
- Bell Peppers – Pack more vitamin C than oranges.
- Broccoli – Antioxidants and fiber for immune support.
- Fatty Fish – Omega‑3 fats reduce inflammation and support immunity.
- Garlic & Ginger – Anti‑inflammatory compounds that enhance immune cell activity.
- Turmeric (Curcumin) – Proven anti‑inflammatory and antioxidant.
- Nuts & Seeds – Vitamin E and trace minerals.
- Green Tea – Catechins with antioxidant properties.
- Yogurt – Probiotic support for gut‑linked immunity.
- Mushrooms – Natural vitamin D and immune support compounds.
These foods work synergistically — eating them regularly matters more than any single “superfood.” Rather than relying on isolated nutrients or supplements alone, aim for variety every day.
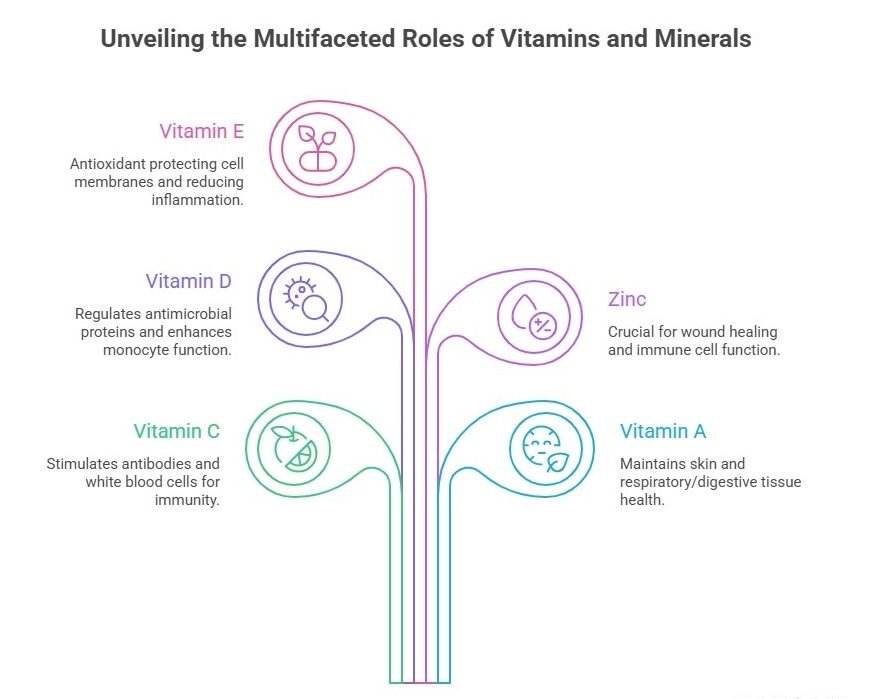
Important Nutrients for Immune Support
| Vitamin | Sources | Role in the Body |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons), bell peppers, strawberries, tomatoes, broccoli | Stimulates the production of antibodies and white blood cells, which are critical for immune defense. It also helps protect cells from damage and supports wound healing. |
| Vitamin A | Sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach, red bell peppers | Helps maintain the health of skin and tissues in the respiratory and digestive systems, acting as a first line of defense against infections. |
| Vitamin D | Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), egg yolks, fortified dairy | Regulates antimicrobial proteins that help kill pathogens. It also enhances the pathogen-fighting effects of monocytes (a type of immune cell). |
| Zinc | Oysters, beef, beans, nuts, poultry | Crucial for wound healing, and the normal function of immune cells. Zinc also helps activate T-lymphocytes (T-cells), essential for immune response. |
| Vitamin E | Almonds, sunflower seeds, vegetable oils | A powerful antioxidant that protects cell membranes from damage, supports immune cell function, and reduces inflammation. |
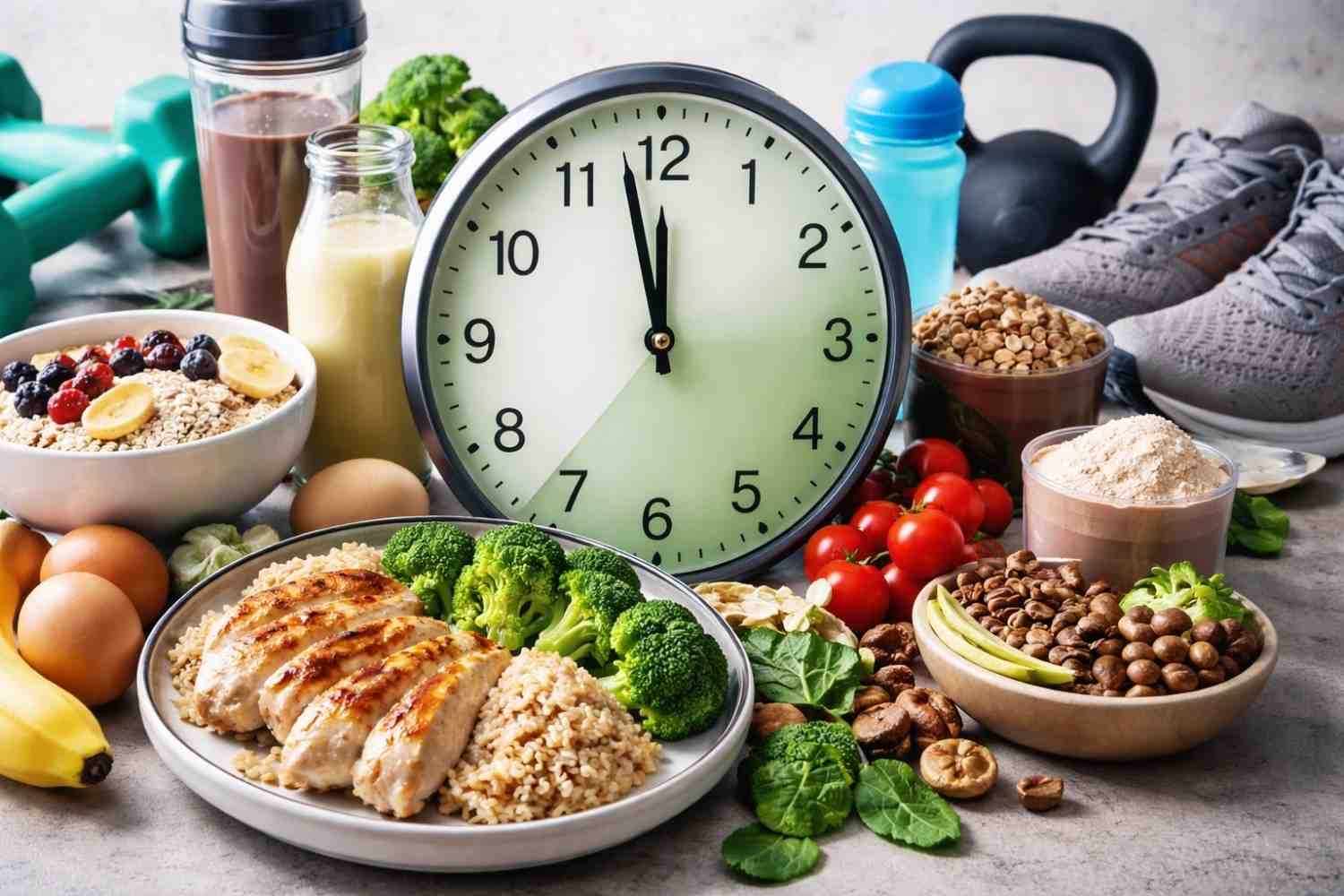
Smart Eating Patterns that Support Immune Function
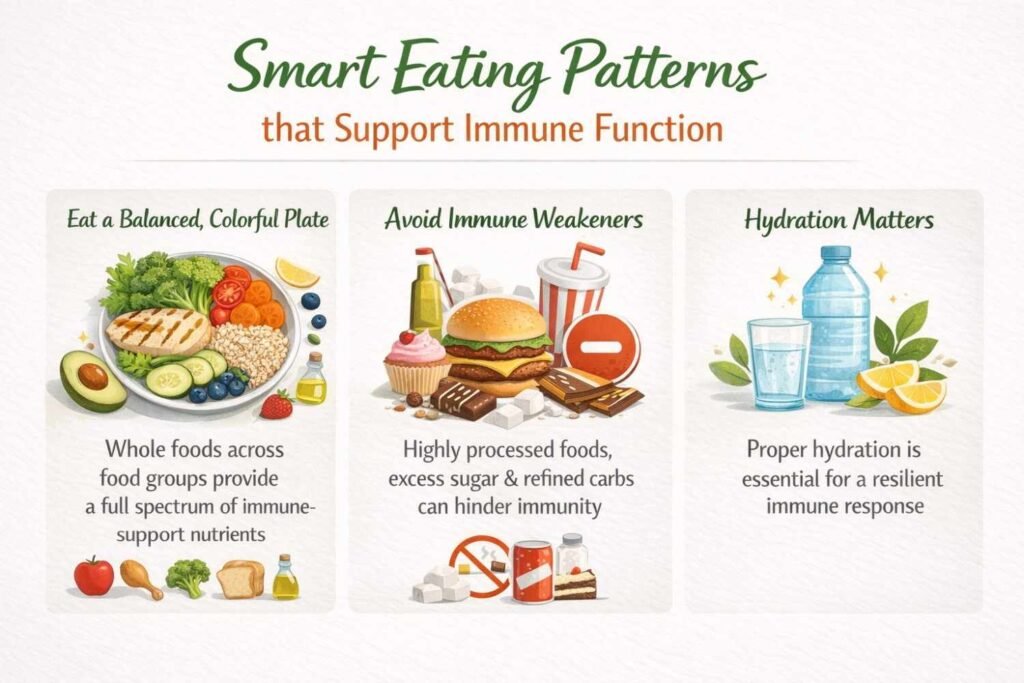
Eat a Balanced, Colorful Plate
A nutrient‑dense plate contains whole foods across food groups — fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. This pattern reliably delivers the full spectrum of immune‑support nutrients.
Avoid Immune Weakeners
Highly processed foods, excess sugar, and refined carbs promote inflammation and can hinder immune responsiveness when consumed too often.
Hydration Matters
Water supports cellular communication, digestion, and detoxification — all foundational for an effective immune response.
Sample Day of Immune‑Boosting Eating
Here’s an example of how to weave immune nutrition into your day:
Breakfast: Greek yogurt with berries and seeds
Lunch: Spinach and bell pepper salad with salmon
Snack: Orange slices and almonds
Dinner: Sweet potato, broccoli, and turmeric‑spiced lentils
Eating nutrient‑dense foods in a routine makes balanced intake easier and more sustainable long term.
Lifestyle Habits That Amplify Nutrition’s Benefits

Nutrition is crucial, but immune health is holistic. The following habits enhance the effect of your food choices:
- Get quality sleep – Immune cells regenerate during sleep.
- Stay active – Moderate exercise boosts immune cell circulation.
- Manage stress – Chronic stress suppresses immunity.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol – Both impair immune function.
Common Reader Questions (FAQs)
1. Does eating these foods prevent infections?
No food guarantees you won’t get sick. But eating nutrient‑rich foods supports immune function so your body is better prepared to defend itself.
2. Can supplements replace a healthy diet?
Supplements can help if you’re deficient, but whole foods deliver a broader range of nutrients and plant compounds that work together more effectively than isolated pills.
3. How soon will I see benefits?
Nutrition affects immune health over time. Consistency over weeks and months delivers the best outcomes — immunity isn’t instant.
Final Thoughts
Boosting your immune system naturally with nutrition isn’t about chasing quick fixes — it’s about daily habits that consistently deliver the building blocks your body needs to stay resilient. Prioritize whole, colorful, nutrient‑dense foods, stay hydrated, and support your diet with healthy lifestyle habits. This balanced approach fuels not only your immune system — but your overall energy and lifelong health.